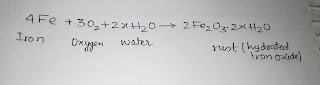EXPERIMENTAL VERIFICATION OF OHM'S LAW
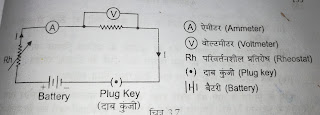
EXPERIMENTAL VERIFICATION OF OHM'S LAW OBJECTIVE:- Verification of ohm's law EQUIPMENT REQUIRED :- A battery, an ammeter, voltmeter, rheostat, plug key, coil, of unknown substance, connecting wire etc. THEORY :- Ohm's law deal with the relationship between voltage (p.d) and current in an ideal conductor. This relationship states that - The p. d.(voltage) across an ideal conductor is directly proportional the current through it. Ohm's law given by V=IR Where, V= potential difference I= current R= constant (Resistance) CIRCUIT DIAGRAM :- PROCEDURE:- 1. The circuit is connected as per the circuit diagram. 2. The plug key is inserted and the rheostat is adjusted so that a definite amount of current (I) flows in the circuit. This value of current is recorded. 3. As the current flows through the unknown resistance a p. d. is developed which is read from voltmeter. 4. The procedure is again adjusted to a different v...